Emergency Response GEIS
Through the integrated information network and communication system, the Emergency Response System GEIS integrates the urban emergency linkage of public security, fire protection, health first aid, transportation, public facilities, natural disasters and other emergencies with the comprehensive social services and scheduling in one management system. Through the sharing of command platform and basic information, it realizes unified alarm reception, unified command, joint action, rapid response, and provides more convenient emergency rescue and related services for citizens, Provide technical support for the government to make scientific decisions and deal with various emergencies and disasters, and provide technical support for urban public safety.
Using multi-agent system technology, a distributed Emergency Response System GEIS is built on the basis of Agent Grid Intelligent Platform AGrIP, which integrates switch oriented CTI middleware, system integration oriented communication middleware and various business oriented standard components to realize the management of resources between heterogeneous systems, the subscription and triggering of resource states, and the state driving of business processes.
Using artificial intelligence technology, according to the 4R Theory of crisis management and C4I command and control theory, expert system, case-based reasoning, data mining, special command and control mathematical model for emergency linkage are used to generate plans and intelligent decision support, so as to ensure the accurate and rapid response ability of emergency linkage command.
The important module of GEIS is the plan generation system. From the perspective of workflow, the generation of the plan starts from the alarm response to emergencies. First, the alarm receiver records and preliminarily analyzes the emergency. If it is a false alarm or minor event, there is no need to start the plan generation system; If it is a major event (such as riots, major fires, floods, and major mining accidents), first report to the superior, and then query the plan base according to the situation to see whether there is an emergency plan. If there is a corresponding solution plan, report the plan to the competent leader in written or electronic format. In the absence of a plan, the simulation solution is obtained by rule reasoning according to the expert system. For general events, such as ordinary traffic accidents, there is generally no need to report, and the competent department directly queries the plan database or handles them according to relevant rules. For the plan that successfully solves the actual problems, add positive feedback to the plan after implementation; For the plan with poor performance in solving practical problems, the plan shall be revised in time according to the feedback.
The plan generation module is mainly composed of two parts: CBR system CbrSys and RBR system OKPS. The CbrSys system searches the database according to the input of the current situation and queries whether there are similar cases. If it exists, its solution will be called as an auxiliary decision-making in this emergency. If the scheme does not exist or the case similarity is very low, the RBR system is called for general rule reasoning. On the one hand, the results are stored in the database as a plan for future use, on the other hand, they are displayed to the user as an auxiliary decision-making of the current event. The structure of the plan generation module is shown in the Figure 1.
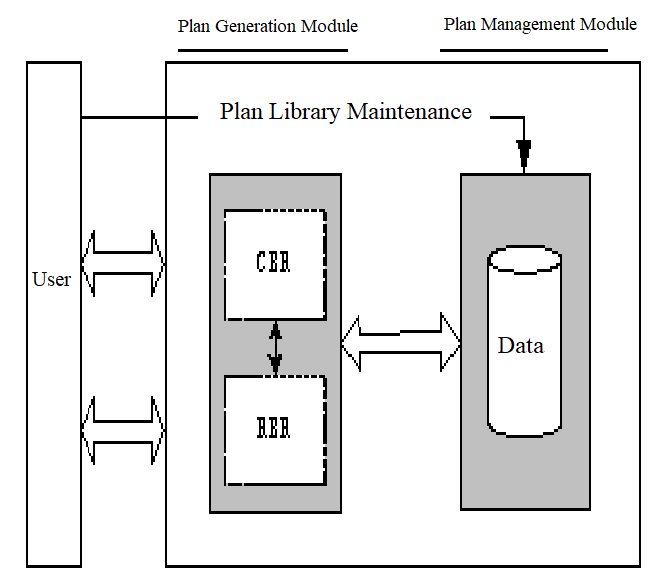
Figure 1 Structure diagram of plan generation module
Download File: